


www@falstad.com
Thanks to Tim Talbert for providing some of the data.
| 1.616x10-35 m | 1.616x10-35 m | the Planck length (the smallest measurement of length that has meaning) |
| 1x10-15 m | 1x10-15 m | one fermi |
| 1.66 fm | 1.66x10-15 m | diameter of proton |
| 2.2 fm | 2.2x10-15 m | classical diameter of neutron |
| 3.8 fm | 3.8x10-15 m | diameter of the nucleus of a helium atom |
| 5.635881 fm | 5.635881x10-15 m | classical diameter of an electron |
| 7.2 fm | 7.2x10-15 m | diameter of the nucleus of an aluminum atom |
| 14 fm | 1.4x10-14 m | diameter of the nucleus of a gold atom |

| 14 fm | 1.4x10-14 m | diameter of the nucleus of a gold atom |
| 1,000 fm | 1x10-12 m | one picometer |
| 1 pm | 1x10-12 m | wavelength of gamma rays |

| 1 pm | 1x10-12 m | wavelength of gamma rays |
| 38 pm | 3.8x10-11 m | diameter of flourine ion |
| 52.9 pm | 5.29x10-11 m | most likely distance from electron to nucleus in a hydrogen atom (bohr radius) |
| 74.13 pm | 7.413x10-11 m | distance between bonded hydrogen atoms |
| 100 pm | 1x10-10 m | one angstrom |
| 120 pm | 1.2x10-10 m | Van Der Waals radius of hydrogen atoms (max distance between atoms that are not bonded) |
| 200 pm | 2x10-10 m | resolution (size of smallest visible object) of a transmission electron microscope |
| 248.2 pm | 2.482x10-10 m | distance between bonded iron atoms |
| 275 pm | 2.75x10-10 m | Van Der Waals radius of potassium atoms (max distance between atoms that are not bonded) |
| 300 pm | 3x10-10 m | diameter of water molecule |
| 340 pm | 3.4x10-10 m | distance between base pairs in a DNA molecule |
| 380 pm | 3.8x10-10 m | diameter of xenon ion |
| 530.9 pm | 5.309x10-10 m | distance between bonded cesium atoms |
| 530.9 pm | 5.309x10-10 m | distance between bonded cesium atoms |
| 1,000 pm | 1x10-9 m | one nanometer |
| 1.5 nm | 1.5x10-9 m | size of glucose molecule |
| 2 nm | 2x10-9 m | diameter of DNA helix |
| 5 nm | 5x10-9 m | diameter of insulin molecule |
| 6 nm | 6x10-9 m | diameter of a hemoglobin molecule |
| 10 nm | 1x10-8 m | thickness of cell wall (gram negative bacteria) |
| 75 nm | 7.5x10-8 m | size of typical virus |
| 125 nm | 1.25x10-7 m | thickness of gold leaf |
| 200 nm | 2x10-7 m | diameter of smallest bacteria |
| 200 nm | 2x10-7 m | resolution (size of smallest visible object) of an optical microscope |
| 260 nm | 2.6x10-7 m | length of the smallest transistor in a Pentium 3 chip |
| 260 nm | 2.6x10-7 m | length of the smallest transistor in a Pentium 3 chip |
| 410 nm | 4.1x10-7 m | wavelength of violet light |
| 680 nm | 6.8x10-7 m | wavelength of red light |
| 1,000 nm | 1x10-6 m | one micrometer (micron) |
| 1 Ám | 1x10-6 m | size of typical bacterium |
| 1 Ám | 1x10-6 m | diameter of sperm cell |
| 1.7 Ám | 1.7x10-6 m | diameter of average human cell nucleus |
| 2.4 Ám | 2.4x10-6 m | thickness of red blood cell |
| 3 Ám | 3x10-6 m | length of the smallest transistor in an Intel 286 chip |
| 4 Ám | 4x10-6 m | diameter of capillary |
| 6 Ám | 6x10-6 m | length of the smallest transistor in an Intel 8086 chip |
| 7 Ám | 7x10-6 m | diameter of a single yeast organism |
| 8.4 Ám | 8.4x10-6 m | diameter of red blood cell |
| 10 Ám | 1x10-5 m | diameter of average cell in human body |
| 10 Ám | 1x10-5 m | size of a grain of talcum powder |
| 16 Ám | 1.6x10-5 m | length of the smallest transistor in the first 6502 chips |
| 16 Ám | 1.6x10-5 m | length of the smallest transistor in the first 6502 chips |
| 20 Ám | 2x10-5 m | length of the smallest transistor in an Intel 4004 (the first microprocessor) |
| 20 Ám | 2.0x10-5 m | diameter of a small grain of sand |
| 25 Ám | 2.5x10-5 m | length of sperm cell |
| 25 Ám | 2.5x10-5 m | diameter of a human hair |
| 83.82 Ám | 8.382x10-5 m | typical thickness of a piece of paper |
| 100 Ám | 1x10-4 m | mimimum size of object the human eye can resolve unaided |
| 100 Ám | 1x10-4 m | diameter of human fertilized egg cell |
| 100 Ám | 1x10-4 m | size of a grain of salt |
| 110 Ám | 1.1x10-4 m | thickness of a dollar bill |
| 300 Ám | 3x10-4 m | diameter of a period on a typewriter |
| 375 Ám | 3.7x10-4 m | diameter of the most common type of optical fiber |
| 750 Ám | 7.5x10-4 m | size of largest known bacterium |
| 1,000 Ám | 1x10-3 m | one millimeter |
| 1.7 mm | 1.7x10-3 m | diameter of the head of the average pin |
| 2 mm | 2x10-3 m | diameter of a large grain of sand |
| 2 mm | 2x10-3 m | diameter of a large grain of sand |
| 2 mm | 2x10-3 m | size of a small ant |
| 4.234 mm | 4.234x10-3 m | height of a line of text in 12-point type |
| 10 mm | 1x10-2 m | one centimeter |
| 1.7 cm | 1.7x10-2 m | wavelength of 20khz note (highest that can be heard) at 27 degrees celsius |
| 2.5 cm | 2.5x10-2 m | size of a large ant |
| 2.54 cm | 2.540x10-2 m | one inch |
| 8.5 cm | 8.5x10-2 m | length of largest human chromosome if it were stretched end-to-end |
| 12.2 cm | 1.22x10-1 m | wavelength of microwaves in a microwave oven |
| 30 cm | 3.0x10-1 m | one foot |
| 79 cm | 7.9x10-1 m | wavelength of 440 hertz note (A above middle C) at 27 degrees celsius |
| 91 cm | 9.1x10-1 m | one yard |
| 1 m | 1 m | one meter |
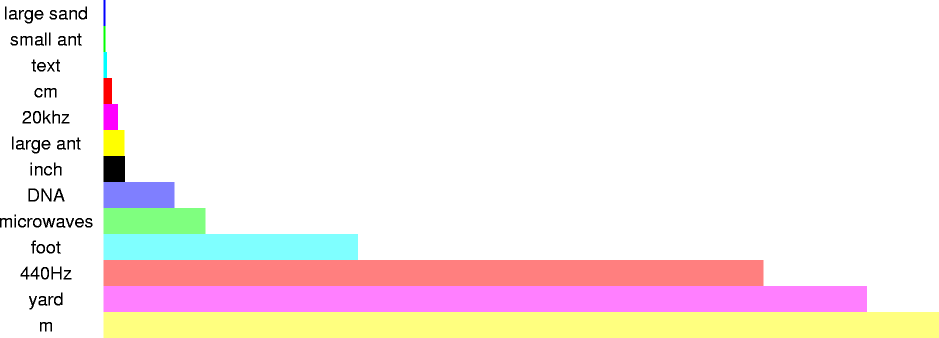
| 1 m | 1 m | one meter |
| 3 m | 3 m | average wavelength of FM radio waves |
| 17 m | 1.7x101 m | wavelength of 20 hertz note (lowest that can be heard) at 27 degrees celsius |
| 299.7925 m | 2.997925x102 m | distance light travels in one microsecond, in a vacuum |
| 343 m | 3.43x102 m | distance sound travels in one second (at 20 degress celsius) |
| 415 m | 4.1x102 m | distance a bullet travels per second, when fired from a .22 |
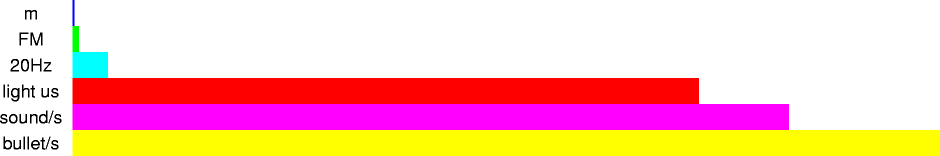
| 415 m | 4.1x102 m | distance a bullet travels per second, when fired from a .22 |
| 1,000 m | 1x103 m | one kilometer |
| 1.609344 km | 1.609344x103 m | one mile |
| 4.3 km | 4.3x103 m | thickness of Greenland ice cap, at thickest point |
| 4.47 km | 4.47x103 m | greatest measured thickness of antarctic ice cap |
| 8.85 km | 8.85x103 m | height of Mount Everest |
| 10.294 km | 1.0294x104 m | depth of Marianas Trench |
| 11 km | 1.1x104 m | average height of top of troposphere (layer of atmosphere affected by weather) |
| 29.78 km | 2.978x104 m | distance the earth travels per second in its orbit |
| 48 km | 4.8x104 m | average height of top of stratosphere (layer of atmosphere containing ozone; free of weather, good for flying) |
| 50 km | 5x104 m | depth of earth's crust |
| 60 km | 6x104 m | thickness of ozone layer |
| 80 km | 8x104 m | height of ionosphere (ionized region which reflects radio waves) |
| 80 km | 8x104 m | average height of top of mesosphere (strong currents, unstable, bad for flying) |
| 160 km | 1x105 m | 100 miles |
| 299.7925 km | 2.997925x105 m | distance light travels in one millisecond, in a vacuum |
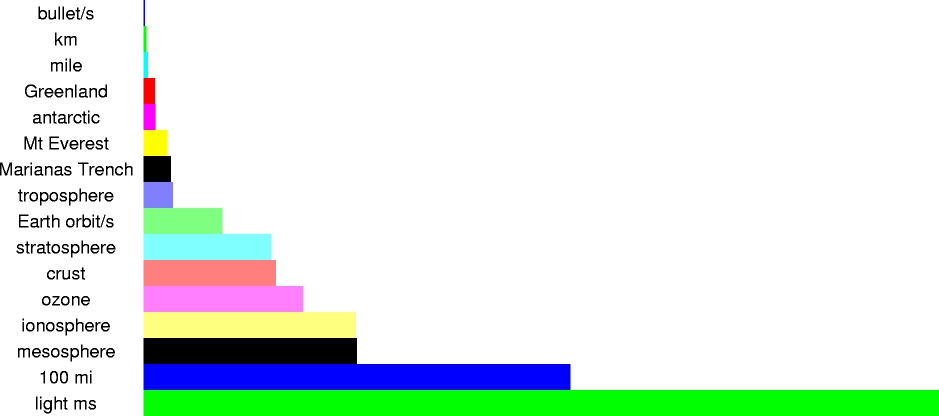
| 299.7925 km | 2.997925x105 m | distance light travels in one millisecond, in a vacuum |
| 300 km | 3x105 m | height of space shuttle's typical orbit |
| 354 km | 3.54x105 m | average altitude of International Space Station |
| 640 km | 6.4x105 m | height of lowest point of inner Van Allen belt |
| 792 km | 7.92x105 m | altitude of Iridium satellites (LEO) |
| 825 km | 8.25x105 m | altitude of Orbcomm satellites (LEO) |
| 914 km | 9.14x105 m | diameter of the asteroid Ceres |
| 1,000 km | 1x106 m | thickness of earth's atmosphere |
| 1,375 km | 1.375x106 m | height of Teledesic (low-earth orbit) satellites |
| 1,414 km | 1.414x106 m | altitude of Globalstar satellites (LEO) |
| 2,274 km | 2.274x106 m | diameter of Pluto at its equator |
| 2,890 km | 2.89x106 m | depth of earth's outer (liquid) core |
| 3,474.8 km | 3.4748x106 m | diameter of moon |
| 3,962 km | 3.962x106 m | distance from New York to Los Angeles |
| 4,879.4 km | 4.8794x106 m | diameter of Mercury at its equator |
| 5,150 km | 5.150x106 m | diameter of Titan |
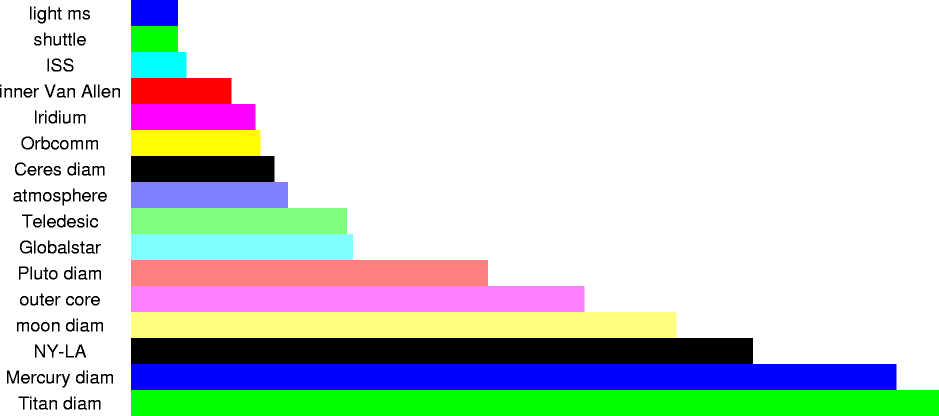
| 5,150 km | 5.150x106 m | diameter of Titan |
| 5,150 km | 5.15x106 m | depth of earth's inner (solid) core |
| 5,200 km | 5.2x106 m | height of highest point of outer Van Allen belt |
| 5,262 km | 5.262x106 m | diameter of Ganymede |
| 5,613 km | 5.613x106 m | distance from New York to London |
| 6,378.14 km | 6.37814x106 m | distance to center of Earth |
| 6,794.4 km | 6.7944x106 m | diameter of Mars at its equator |
| 9,084 km | 9.084x106 m | distance from London to Los Angeles |
| 9,380 km | 9.38x106 m | mean distance from Phobos to Mars |
| 10,390 km | 1.039x107 m | altitude of ICO satellites (MEO) |
| 12,103 km | 1.2103x107 m | diameter of Venus at its equator |
| 12,756.2 km | 1.27562x107 m | diameter of Earth at its equator |
| 20,200 km | 2.02x107 m | altitude of GPS satellites |
| 23,460 km | 2.346x107 m | mean distance from Deimos to Mars |
| 35,800 km | 3.58x107 m | height of satellite in geostationary orbit |
| 47,810 km | 4.781x107 m | min initial altitude of Geotail satellite (VHO) |
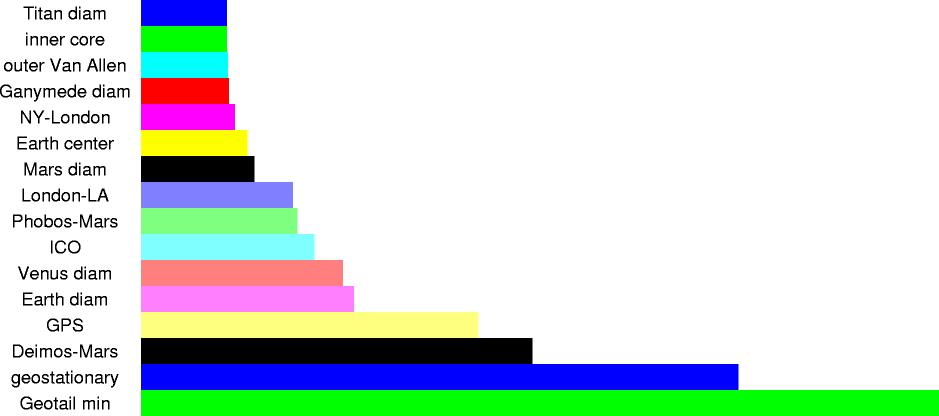
| 47,810 km | 4.781x107 m | min initial altitude of Geotail satellite (VHO) |
| 49,492 km | 4.9492x107 m | diameter of Neptune at its equator |
| 51,118 km | 5.1118x107 m | diameter of Uranus at its equator |
| 120,536 km | 1.2053x108 m | diameter of Saturn at its equator |
| 142,984 km | 1.4298x108 m | diameter of Jupiter at its equator |
| 299,792.5 km | 2.997925x108 m | distance light travels in one second, in a vacuum |
| 384,400 km | 3.844x108 m | mean distance from earth to moon |
| 868,912 km | 8.68912x108 m | max initial altitude of Geotail satellite (VHO) |
| 1,070,000 km | 1.07x109 m | mean distance from Jupiter to Ganymede |
| 1,221,850 km | 1.22185x109 m | mean distance from Saturn to Titan |
| 1,390,000 km | 1.39x109 m | diameter of sun at its equator |
| 1,500,000 km | 1.5x109 m | distance to SOHO satellite (L1 Lagrange point) |
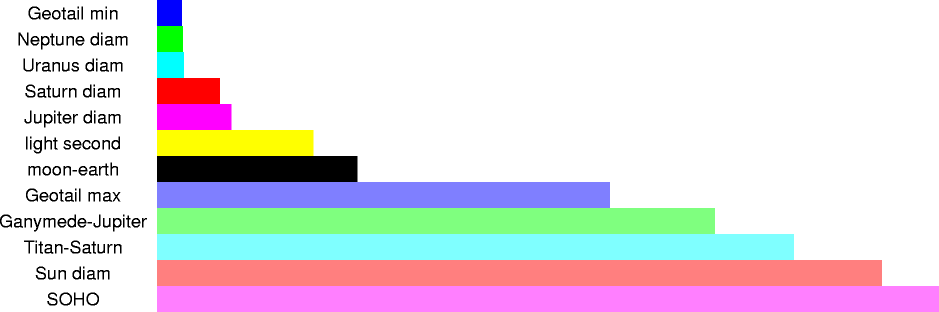
| 1,500,000 km | 1.5x109 m | distance to SOHO satellite (L1 Lagrange point) |
| 17,987,550 km | 1.798755x1010 m | distance light travels in one minute, in a vacuum |
| 57,910,000 km | 5.791x1010 m | mean distance of Mercury from the sun |
| 108,200,000 km | 1.082x1011 m | mean distance of Venus from the sun |
| 1 AU | 1x1011 m | mean distance of Earth from the sun (one astronomical unit) |
| 1.5236 AU | 2.2794x1011 m | mean distance of Mars from the sun |
| 2.766 AU | 4.139x1011 m | mean distance of the asteroid Ceres from the sun |
| 5.2028 AU | 7.7833x1011 m | mean distance of Jupiter from the sun |
| 7.2143607 AU | 1.079253x1012 m | distance light travels in one hour, in a vacuum |
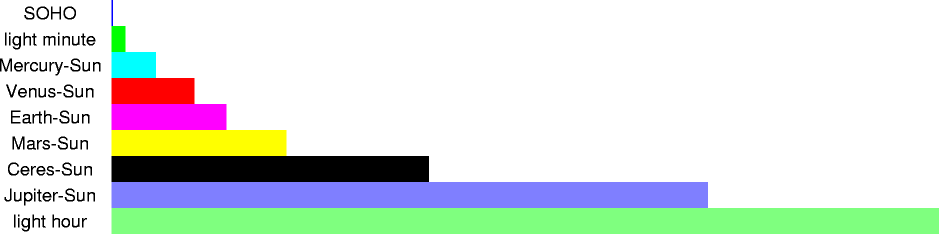
| 7.2143607 AU | 1.079253x1012 m | distance light travels in one hour, in a vacuum |
| 9.5549 AU | 1.4294x1012 m | mean distance of Saturn from the sun |
| 19.1913 AU | 2.87099x1012 m | mean distance of Uranus from the sun |
| 30.109 AU | 4.5043x1012 m | mean distance of Neptune from the sun |
| 34 AU | 5.2x1012 m | maximum distance of Halley's Comet from the sun |
| 39.5294 AU | 5.91352x1012 m | mean distance of Pluto from the sun |
| 43.8 AU | 6.56x1012 m | distance of QB1 object from Sun |
| 62.32 AU | 9.323x1012 m | current distance of Voyager 2 from sun (as of 10/27/00) |
| 79.125 AU | 1.1837x1013 m | current distance of Voyager 1 from sun (as of 10/27/00) |
| 80 AU | 1x1013 m | termination shock--point at which solar wind becomes subsonic |
| 134 AU | 2.0x1013 m | heliopause (outer edge of Sun's magnetic field) |
| 134 AU | 2.01x1013 m | distance of 1996 TL66 object from Sun |
| 173.14464 AU | 2.590207x1013 m | distance light travels in one day, in a vacuum |
| 372 AU | 5.56x1013 m | maximum distance of comet Hale-Bopp from the sun |
| 1,212.0125 AU | 1.813145x1014 m | distance light travels in one week, in a vacuum |

| 1,212.0125 AU | 1.813145x1014 m | distance light travels in one week, in a vacuum |
| 25,000 AU | 3.7x1015 m | possible distance of Sol B from Sun |
| 63,239.737 AU | 9.460530x1015 m | distance light travels in one year (one light-year) |
| 1.5 ly | 1.4x1016 m | possible edge of Oort cloud |
| 3.26 ly | 3.08x1016 m | one parsec |
| 4.22 ly | 3.99x1016 m | distance to the star Proxima Centauri (nearest star other than sun) |
| 4.3 ly | 4.1x1016 m | distance to the stars Alpha Centauri A and B |
| 8.6 ly | 8.1x1016 m | distance to the star Sirius |
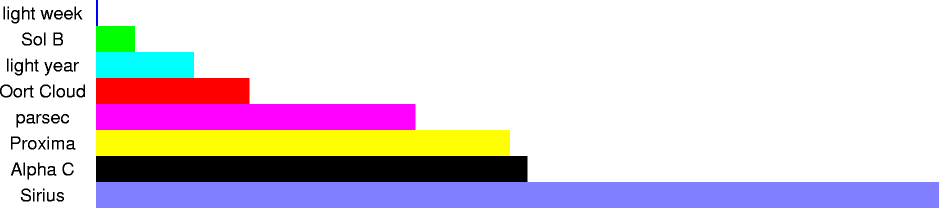
| 8.6 ly | 8.1x1016 m | distance to the star Sirius |
| 25.2 ly | 2.39x1017 m | distance to the star Vega |
| 33 ly | 3.2x1017 m | distance to the star Pollux |
| 36 ly | 3.5x1017 m | distance to the star Arcturus |
| 51 ly | 4.9x1017 m | distance to the star Castor |
| 77 ly | 7.3x1017 m | distance to the star Regulus |
| 300 ly | 2x1018 m | thickness of Milky Way Galaxy |
| 430 ly | 4.0x1018 m | distance to the star Polaris |
| 1.6 kly | 1.5x1019 m | distance to Horsehead Nebula |

| 1.6 kly | 1.5x1019 m | distance to Horsehead Nebula |
| 20 kly | 1x1020 m | diameter of Large Magellanic Cloud galaxy |
| 27 kly | 2.6x1020 m | distance to center of Milky Way Galaxy |
| 44 kly | 4.2x1020 m | diameter of M33 galaxy |
| 162 kly | 1.54x1021 m | diameter of Milky Way Galaxy |
| 200 kly | 1x1021 m | distance to Large Magellanic Cloud galaxy |
| 200 kly | 1x1021 m | diameter of M31 galaxy |
| 300 kly | 2x1021 m | distance to Small Magellanic Cloud galaxy |
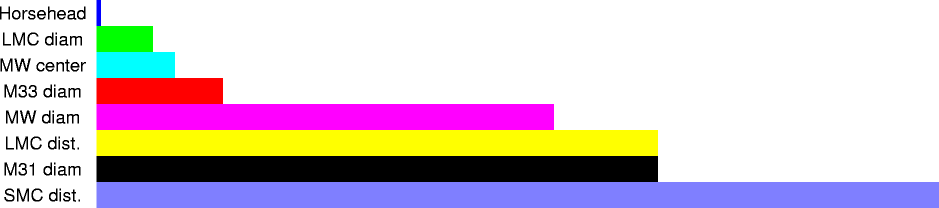
| 300 kly | 2x1021 m | distance to Small Magellanic Cloud galaxy |
| 2,200 kly | 2.0x1022 m | distance to Andromeda galaxy |
| 3,000 kly | 2x1022 m | distance to Pisces galaxy |
| 4,000 kly | 3x1022 m | distance to IC 10 galaxy |
| 5,000 kly | 4x1022 m | distance to Pegasus galaxy |
| 11,000 kly | 1.0x1023 m | distance to the M81 galaxy cluster |
| 15,000 kly | 1.4x1023 m | distance to the M83 galaxy |
| 27,000 kly | 2.5x1023 m | distance to the M101 galaxy |
| 35,000 kly | 3.3x1023 m | distance to the M66 galaxy cluster |
| 37,000 kly | 3.5x1023 m | distance to the M51 galaxy cluster |
| 38,000 kly | 3.5x1023 m | distance to the M95 galaxy |
| 41,000 kly | 3.8x1023 m | distance to the M96 galaxy |
| 60,000 kly | 5x1023 m | distance to the Virgo galaxy cluster |
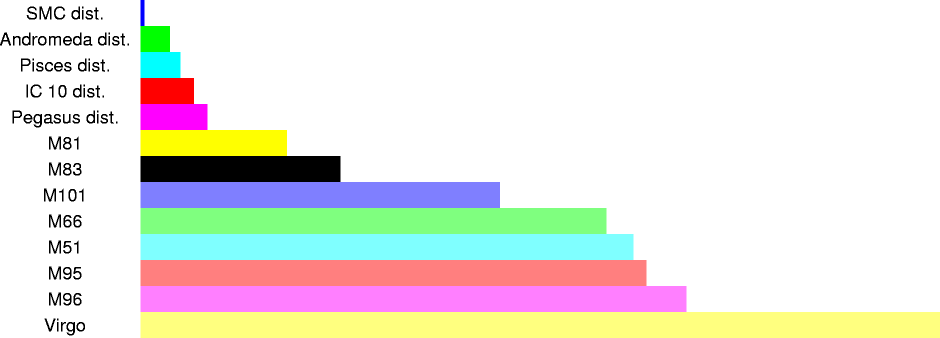
| 60,000 kly | 5x1023 m | distance to the Virgo galaxy cluster |
| 340,000 kly | 3.2x1024 m | distance to the Coma galaxy cluster |
| 2,000,000 kly | 1x1025 m | distance to brightest quasar (3C 273) |
| 4,000,000 kly | 3x1025 m | distance to quasar 3C 48 |
| 26,000,000 kly | 2.4x1026 m | distance to farthest known object (quasar SDSS_1044_0125) |
